Supersonic X-59 shall come for commercial with 1,510 km/h
X-59 May Change the Future of High-Speed Flight
The Lockheed Martin X-59 Quesst (“Quiet SuperSonic Technology”), sometimes styled QueSST, is an American experimental supersonic aircraft being developed at Skunk Works for NASA‘s Low-Boom Flight Demonstrator project. Preliminary design started in February 2016, with the X-59 planned to begin flight testing in 2021. After delays, as of January 2024, it is planned to be delivered to NASA for flight testing in 2024. It is expected to cruise at Mach 1.42 (1,510 km/h; 937 mph) at an altitude of 55,000 ft (16,800 m), creating a low 75 effective perceived noise level (EPNdB) thump to evaluate supersonic transport acceptability.
In February 2016, Lockheed Martin was awarded a preliminary design contract, aiming to fly in the 2020 timeframe. A 9% scale model was to be wind tunnel tested from Mach 0.3 to Mach 1.6 between February and April 2017.
On April 2, 2018, NASA awarded Lockheed Martin a $247.5 million contract to design, build and deliver in late 2021 the Low-Boom X-plane. On June 26, 2018, the US Air Force informed NASA it had assigned the X-59 QueSST designation to the demonstrator.
From November 5, 2018, NASA was to begin tests over two weeks to gather feedback up to eight thumps a day at various locations to be monitored by 20 noise sensors and described by 400 residents.
In May 2019, the initial major structural parts were loaded in the tooling assembly. In June, assembly was getting underway.
NASA reported the installation of the General Electric F-414-GE-100 engine on the X-59, which took place at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works in Palmdale, California early November 2022. The engine is 13 feet (4.0 m) long and produces 98 kN of thrust.
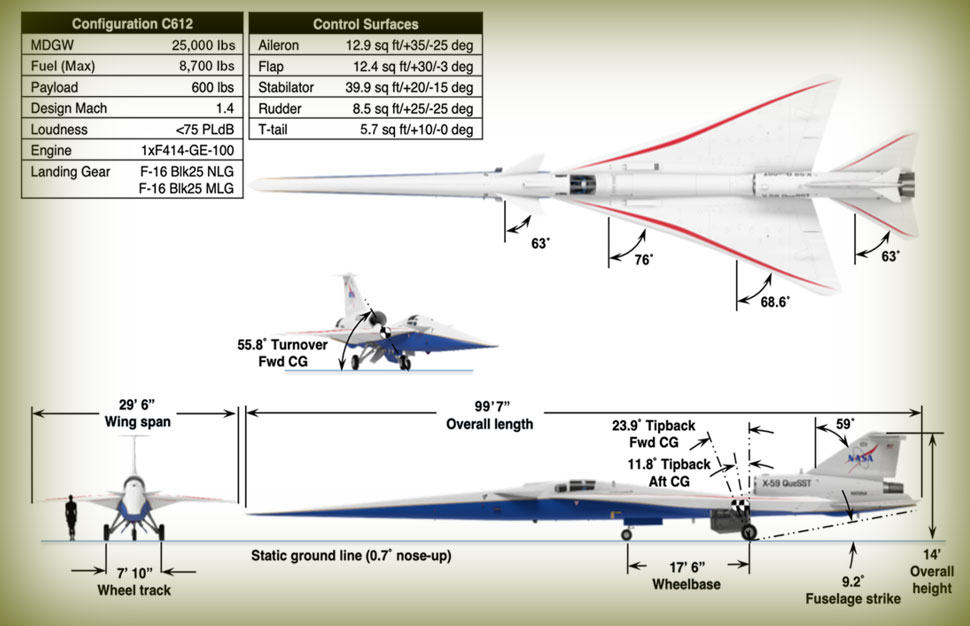
The Low-Boom X-59 plane is 99.7 ft (30.4 m) long with a 29.5 ft (9.0 m) wingspan for a maximum take-off weight of 32,300 lb (14,700 kg). Propelled by a General Electric F-414 engine, it should reach a maximum speed of Mach 1.5 or 990 mph (1,590 km/h), and cruise at Mach 1.42 or 940 mph (1,510 km/h) at 55,000 ft (16,800 m). The cockpit, ejection seat and canopy come from a Northrop T-38 and the landing gear from an F-16. With afterburner, its engine will provide 22,000 lbf of thrust. the X-59’s first flight is planned for 2024.
As of 2017, the ground noise was expected to be around 60 dB(A), about 1/1000 as loud as current supersonic aircraft and NASA hopes the ban on commercial supersonic flight over land can be lifted by replacing the loud sonic boom with a softer sonic “thump.”
The model will travel to Tokyo in March 2024 for additional wind tunnel verification testing with the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency and Boeing so could pave the way for future commercial supersonic flights over land and potentially reduce travel time as half.
WikipediA + NASA

